How Do You Know if You Have a Braind Tumor
There are over 120 encephalon tumor types, based on the brain tissues they touch. Not all brain tumors are encephalon cancer, but fifty-fifty beneficial (or noncancerous) tumors tin can be dangerous because of their size or location.
What is a encephalon tumor?
A brain tumor is a growth of abnormal cells in the brain. The anatomy of the brain is very complex, with dissimilar parts responsible for different nervous system functions. Brain tumors can develop in any part of the brain or skull, including its protective lining, the underside of the brain (skull base), the brainstem, the sinuses and the nasal cavity, and many other areas. There are more than 120 unlike types of tumors that tin develop in the brain, depending on what tissue they arise from.
How common are brain tumors, and are they unsafe?
In the United States, brain and nervous organization tumors bear on about 30 adults out of 100,000. Brain tumors are dangerous because they can put pressure on healthy parts of the brain or spread into those areas. Some encephalon tumors can also be cancerous or get malignant. They can cause problems if they block the flow of fluid around the brain, which can pb to an increment in pressure within the skull. Some types of tumors can spread through the spinal fluid to distant areas of the brain or the spine.
Related Video
Brain Tumors: Oft Asked Questions | Jon Weingart, M.D.
How is a tumor unlike from a brain lesion?
A encephalon tumor is a specific type of brain lesion. A lesion describes any expanse of damaged tissue. All tumors are lesions, but not all lesions are tumors. Other brain lesions can be acquired past stroke, injury, encephalitis and arteriovenous malformation.
Brain Tumor vs. Brain Cancer
All brain cancers are tumors, merely not all encephalon tumors are cancerous. Noncancerous brain tumors are called beneficial encephalon tumors.
Benign encephalon tumors typically grow slowly, have distinct borders and rarely spread. Benign tumors can still be dangerous. They tin damage and compress parts of the brain, causing astringent dysfunction. Benign brain tumors located in a vital expanse of the brain can be life-threatening. Very rarely, a benign tumor can become cancerous. Examples of typically benign tumors include meningioma, vestibular schwannoma and pituitary adenoma.
Malignant brain tumors are cancerous. They typically grow apace and invade surrounding healthy brain structures. Brain cancer can exist life-threatening due to the changes it causes to the vital structures of the encephalon. Some examples of malignant tumors that originate in or most the encephalon include olfactory neuroblastoma, chondrosarcoma and medulloblastoma.
Main vs. Metastatic Encephalon Tumors
Primary brain tumors are tumors that start in the brain. Examples of tumors that most ofttimes originate in the encephalon include meningioma and glioma. Very rarely, these tumors can break abroad and spread to other parts of the brain and spinal cord. More usually, tumors spread to the brain from other parts of the body.
Metastatic brain tumors, besides called secondary brain tumors, are cancerous tumors that originate as cancer elsewhere in the body and and so metastasize (spread) to the encephalon. Metastatic brain tumors are almost four times more mutual than chief brain tumors. They tin grow speedily, crowding or invading nearby brain tissue.
Common cancers that can spread to the encephalon are:
- Breast cancer
- Colon cancer
- Kidney cancer
- Lung cancer
- Skin cancer (melanoma)
Encephalon Tumor Locations
Brain tumors can form in whatever function of the brain, but at that place are certain regions where specific tumors form:
- Meningiomas course in the meninges, the protective lining of the encephalon.
- Pituitary tumors develop in the pituitary gland.
- Medulloblastoma tumors arise from the cerebellum or brainstem.
- Skull base tumors grow on the underside of the brain, called the skull base.
Other brain tumors are described by the kinds of cells they are made of. For example, gliomas are equanimous of glial cells.
Acquire more nigh these and other encephalon tumor types.
Brain Tumors in Children
Brain tumors are the most common solid tumor in children and adolescents, affecting nigh 5,000 children in the U.Southward. each year. Several different types of encephalon tumors can occur in children, including astrocytomas (east.g., glioblastoma multiforme), gliomas, ependymomas and medulloblastomas.
Larn more about brain tumors in children.
Brain Tumor Symptoms
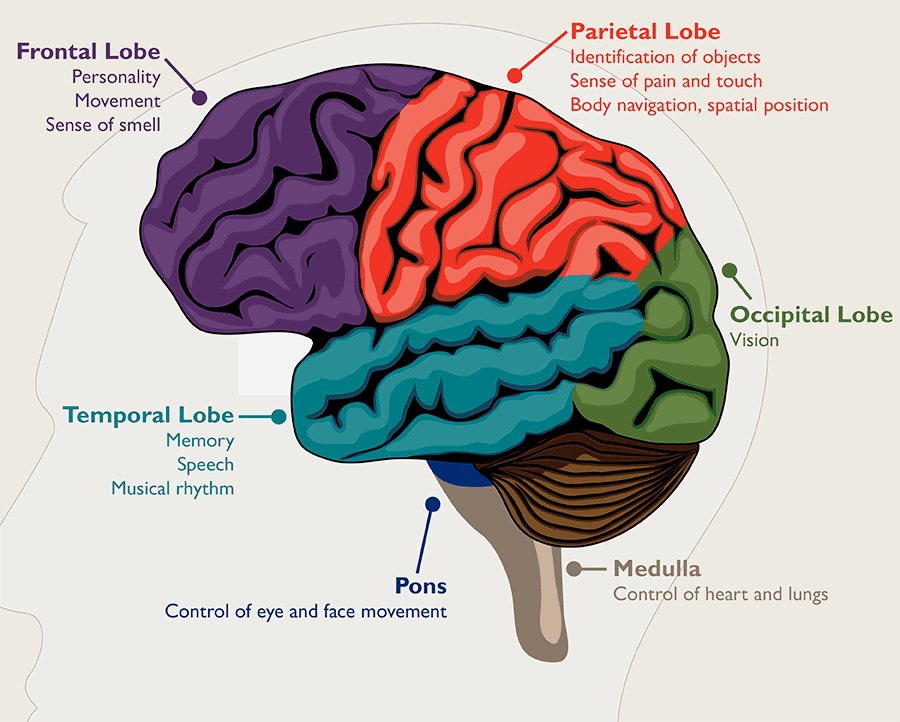
Different parts of the brain control dissimilar functions, so brain tumor symptoms will vary depending on the tumor's location. For example, a brain tumor located in the cerebellum at the dorsum of the head may cause trouble with movement, walking, balance and coordination. If the tumor affects the optic pathway, which is responsible for sight, vision changes may occur.
The tumor's size and how fast it'due south growing also affect which symptoms a person will experience.
In general, the most mutual symptoms of a brain tumor may include:
- Headaches
- Seizures or convulsions
- Difficulty thinking, speaking or finding words
- Personality or behavior changes
- Weakness, numbness or paralysis in ane part or i side of the body
- Loss of residue, dizziness or unsteadiness
- Loss of hearing
- Vision changes
- Confusion and disorientation
- Memory loss
Tin you have a brain tumor with no symptoms?
Encephalon tumors don't always crusade symptoms. In fact, the most common brain tumor in adults, meningioma, often grows and so slowly that information technology goes unnoticed. Tumors may non start causing symptoms until they go large enough to interfere with good for you tissues inside the brain.
Related Video
Convexity Meningioma | A Hollywood Stuntwoman's Story
Brain Tumor Causes and Adventure Factors
Doctors don't know why some cells begin to grade into tumor cells. It may have something to do with a person'due south genes or his or her environment, or both. Some potential brain tumor causes and risk factors may include:
- Cancers that spread from other parts of the body
- Certain genetic conditions that predispose a person to overproduction of certain cells
- Exposure to some forms of radiation
Are brain tumors hereditary?
Genetics are to arraign for a small number (fewer than 5%) of brain tumors. Some inherited conditions put individuals at greater risk of developing tumors, including:
- Neurofibromatosis
- Von Hippel-Lindau disease
- Li-Fraumeni syndrome
- Familial adenomatous polyposis
- Lynch syndrome
- Basal cell nevus syndrome (Gorlin syndrome)
- Tuberous sclerosis
- Cowden syndrome
Brain Tumor Diagnosis
Diagnosing a brain tumor usually involves a neurological exam, brain scans and a biopsy, if it can be done safely.
- A neurological test may include a diverseness of tests to evaluate neurological functions such every bit rest, hearing, vision and reflexes.
- A variety of imaging techniques, including CT (or CAT) browse, MRI, occasionally an angiogram or X-rays tin be used to identify the tumor, pinpoint its location and/or assess the function of your brain.
- If doctors cannot safely perform a biopsy (tissue sample drove and analysis), they will diagnose the brain tumor and plan the handling based on other exam results. If a biopsy was possible, doctors can use it to make up one's mind the tumor class (how ambitious it is), too every bit written report the tumor tissue for whatsoever biomarkers that can help personalize the treatment arroyo.
Depending on your symptoms, doctors may besides perform these tests to help confirm the diagnosis and rule out other conditions:
- Lumbar puncture to collect a sample of cerebrospinal fluid and encounter if it contains traces of the tumor cells.
- Evoked potentials studies to measure electrical activity in the nerves and/or electroencephalography (EEG) to measure electrical activity in the brain.
- Neurocognitive assessment to evaluate whatsoever changes in cognition and well-being.
- Neuro-ophthalmological examination to assess for signs of tumor affecting the optics.
- Endocrinological evaluation to appraise hormone part.
Proper diagnosis is essential in determining the best course of handling.
Encephalon Tumor Grading
The grade of a brain tumor defines how serious it is. Using the biopsy sample, a pathologist volition examine the tumor nether a microscope to determine its grade. Brain tumor grading is a category system that describes the brain tumor cells and indicates how probable the tumor is to abound and spread.
Encephalon tumor grading uses a scale from 1 (least ambitious) to 4 (most aggressive).
(Globe Health Organization tumor grading arrangement)
Grade I brain tumor
- Benign (noncancerous)
- Slow-growing
- Cells look almost normal under a microscope
- Ordinarily associated with long-term survival
- Rare in adults
Grade II brain tumor
- Relatively slow-growing
- Sometimes spreads to nearby normal tissue and comes back (recurs)
- Cells await slightly aberrant under a microscope
- Sometimes comes back as a higher grade tumor
Grade Iii encephalon tumor
- Cancerous (cancerous)
- Actively reproduces aberrant cells
- Tumor spreads into nearby normal parts of the encephalon
- Cells look aberrant under a microscope
- Tends to come dorsum, often as a college grade tumor
Grade 4 brain tumor
- Malignant
- Most aggressive
- Grows fast
- Hands spreads into nearby normal parts of the brain
- Actively reproduces abnormal cells
- Cells await very abnormal under a microscope
- Tumor forms new blood vessels to maintain rapid growth
- Tumors have areas of dead cells in their centre (chosen necrosis)
A changing diagnosis
The class of a brain tumor might change, usually to a higher course, often without a cause. It's as well possible that the biopsy sample might not correspond the entire tumor, giving an inaccurate initial data for the course.
A change from a low-grade tumor to a high-grade tumor happens more often in adults than in children.
Brain Tumor Staging
Staging refers to how far a tumor has spread. If a tumor has migrated to other parts of the trunk, information technology has metastasized. Staging is often done for other types of tumors but non primary brain tumors. This is because brain tumors are unlikely to spread beyond the nervous organisation.
Conversely, other types of tumors (e.g., lung cancer) can spread to the brain. Tumors that have spread to the brain are avant-garde stage.
What does the size of a encephalon tumor hateful?
Because larger tumors are more likely to interfere with normal brain office, they more ofttimes cause symptoms and complications.
Brain Tumor Treatment
The nigh common treatment for encephalon tumors is surgery. For some tumors, surgical removal and continued monitoring may be the only treatment needed. Common surgical approaches to encephalon tumor removal include craniotomy, neuroendoscopy, laser ablation and laser interstitial thermal therapy.
Chemotherapy and radiation therapy tin can be used to treat brain cancer by helping shrink the tumor, slowing down its growth and/or preventing it from coming back. External axle radiation therapy, stereotactic radiosurgery and proton therapy are some of the radiation treatments for brain tumor.
Learn more well-nigh these and other encephalon tumor treatment options.

The Johns Hopkins Brain Tumor Center
The Johns Hopkins Comprehensive Brain Tumor Center is i of the largest brain tumor treatment and research centers in the world. Nosotros tailor each patient's treatment using an array of advanced approaches, including emerging treatments such as tumor-treating fields and MRI-guided light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation ablation.
Encephalon Tumor Prognosis
Brain tumor can be a frightening diagnosis. It's important to partner with a medical team yous trust to determine the all-time next steps, whether information technology's ascertainment, surgery, radiations therapy or another treatment. How successful your personal outcome will be depends on many factors, including:
- The blazon of brain tumor, its size, class and location
- Whether the tumor has spread within the encephalon or to other parts of the torso
- Your age and overall wellness
- How long you lot had symptoms before you were diagnosed with a brain tumor
- How much the brain tumor affects your ability to part
- Your handling preferences
- The expertise of your treatment team
In that location is no projected survival charge per unit for those diagnosed with a brain tumor, as private circumstances play a big role. For case, some cancerous tumors can be successfully controlled by radiation therapy. Others, considering of their location, may be life-threatening even if they are benign. Doctors take to expect at thousands of patients with similar characteristics to see a trend in how sure tumors progress and how different treatments bear upon them.
Your overall outlook and prognosis are likely to change every bit yous undergo diverse treatments. If you have surgery, how much of the tumor the neurosurgeon can remove volition touch what will happen adjacent. Other brain tumor treatments will make up one's mind future steps as well.
Source: https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/brain-tumor
0 Response to "How Do You Know if You Have a Braind Tumor"
Post a Comment